Minor version update¶
Assuming operator-level familiarity with the minor updates, let’s look at individual pieces in more detail.
How update commands work¶
The following subsections describe the individual update commands:
You might also find it helpful to consult this high-level diagram as you read:
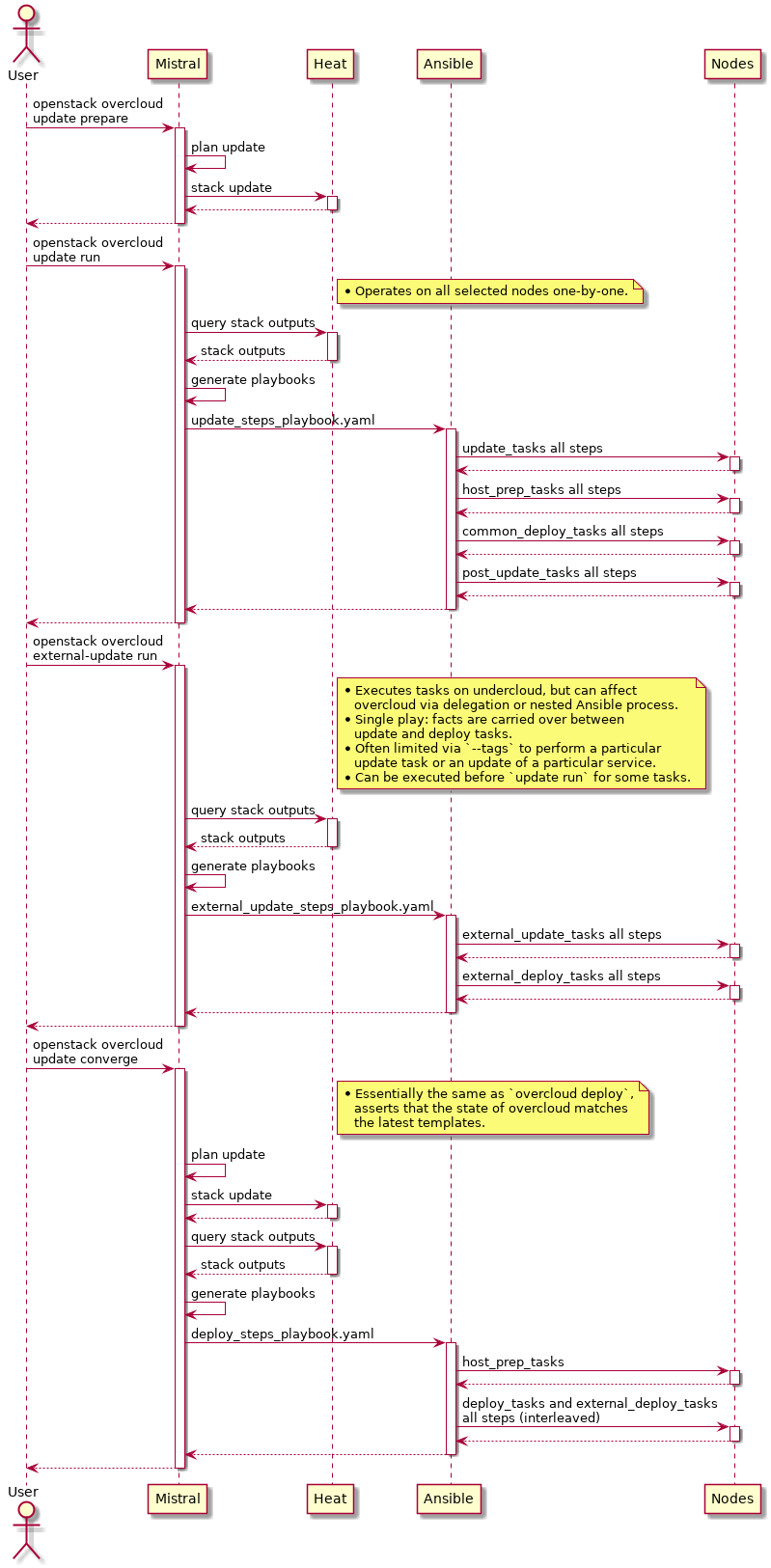
openstack overcloud update prepare¶
The update prepare command performs a Heat stack update, mapping
some resources to OS::Heat::None in order to prevent the usual
deployment config management tasks being performed (running Puppet,
starting containers, running external installers like
ceph-ansible). See the update prepare environment file.
The purpose of this stack update is to regenerate fresh outputs of the Heat stack. These outputs contain Ansible playbooks and task lists which are then used in the later in the update run phase.
openstack overcloud update run¶
The update run command utilizes the previously generated Heat stack outputs. It downloads the playbook yamls and their included task list yaml via the config-download mechanisms, and executes the update steps playbook.
The command accepts --nodes or --roles argument to limit which
nodes will be targeted during a particular update run
execution. Even if the limit matches multiple nodes (e.g. all nodes
within one role), the play is executed with serial: 1, meaning
that all actions are finished on one node before starting the update
on another.
The play first executes update_steps_tasks.yaml which are tasks
collected from the update_tasks entry in composable
services.
After the update tasks are finished, deployment workflow is
performed on the node being updated. That means reusing
host_prep_tasks.yaml and common_deploy_steps_tasks.yaml, which are
executed like on a fresh deployment, except during minor update
they’re within a play with the aforementioned serial: 1 limiting.
Finally, post_update_tasks are executed. They are utilized by
services which need to perform something after deployment workflow
during the minor update. The update of the node is complete and the
Ansible play continues to update another node.
openstack overcloud external-update run¶
The external-update run command is used to update the services whose deployment (and update) procedure is not tied to execution on particular overcloud nodes. The deployment/update procedures are thus executed from the undercloud, even though a full overcloud inventory is available for use.
The external update playbook first executes external_update_tasks and then external_deploy_tasks. The execution happens within the same Ansible play, so facts from external_update_tasks are carried over to external_deploy_tasks. This is a mechanism which will allow you to amend what your deploy tasks do based on whether an update is being run or not.
Often it’s not desirable to run the tasks for all services at the same
time, so external-update run supports --tags argument to limit
which tasks are run.
The mechanisms of external-upgrade and external-update commands and Ansible tasks are the same, but two commands and task hooks are provided because generally in OpenStack we distinguish minor update vs. major upgrade workflows. If your service only has one type of upgrade, you can make the external_update_tasks the same as external_upgrade_tasks by using YAML anchors and references.
openstack overcloud update converge¶
Note
Update Converge is only required for versions less than Wallaby. Update Converge has been removed for Wallaby and beyond.
The update converge command performs a Heat stack update, reverting
the previous OS::Heat::None resource mappings back to the values
used for regular deployments and configuration updates, and
potentially also resets some parameter values. For environments with
Ceph, majority of this already happened on ceph-upgrade run, so the
final update converge effectively just resets the
CephAnsiblePlaybook parameter.
See the update converge environment file.
The purpose of this stack update is to re-run config management mechanisms and assert that the overcloud state matches what is provided by the templates and environment files.
Writing update logic for a service¶
Simple config/image replacement¶
If the service is managed by Paunch or tripleo_container_manage Ansible role,
it may be that there’s no need to write any update tasks. Paunch or
tripleo_container_manage can automatically handle simple updates: change in
configuration or change of container image URL triggers automatic removal of
the old container and creation of new one with latest config and latest image.
If that’s all the service needs for updates, you don’t need to create any
update_tasks.
Custom tasks during updates¶
If the service is not managed by Paunch nor tripleo_container_manage, or if the simple container replacement done by Paunch is not sufficient for the service update, you will need to include custom update logic. This is done via providing these outputs in your composable service template:
update_tasks– these are executed before deployment tasks on the node being updated.post_update_tasks– these are executed after deployment tasks on the node being updated.
Update tasks are generally meant to bring the service into a stopped state (sometimes with pre-fetched new images, this is necessary for services managed by Pacemaker). Then the same workflow as during deployment is used to bring the node back up into a running state, and the post-update tasks can then perform any actions needed after the deployment workflow.
Similarly as deployment tasks, the update tasks and post-update tasks are executed in steps.
