Configure the database with dbconfig-common¶
Many of the OpenStack services need to be configured to access a database. These are configured through a DSN (Database Source Name) directive as follows:
[database]
connection = mysql+pymysql://keystone:0dec658e3f14a7d@localhost/keystonedb
This connection directive will be handled by the dbconfig-common
package, which provides a standard Debian interface. It enables you to
configure Debian database parameters. It includes localized prompts for
many languages and it supports the following database backends: SQLite,
MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
By default, the dbconfig-common package configures the OpenStack
services to use SQLite. So if you use debconf in non-interactive mode
and without pre-seeding, the OpenStack services that you install will
use SQLite.
By default, dbconfig-common does not provide access to database servers
over a network. If you want the dbconfig-common package to prompt for
remote database servers that are accessed over a network and not through
a UNIX socket file, reconfigure it, as follows:
# apt-get install dbconfig-common && dpkg-reconfigure dbconfig-common
These screens appear when you re-configure the dbconfig-common package:
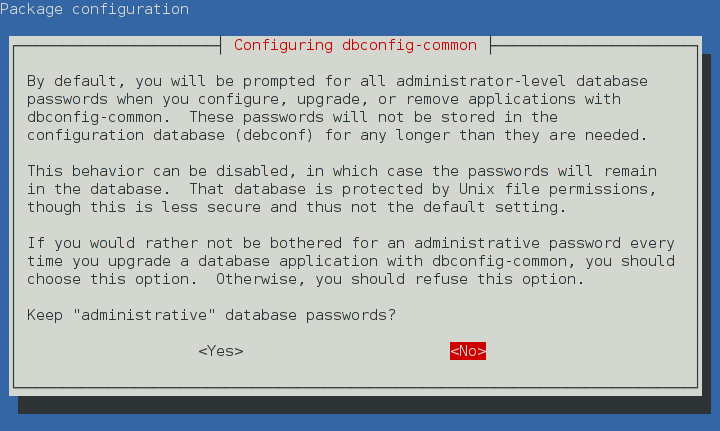
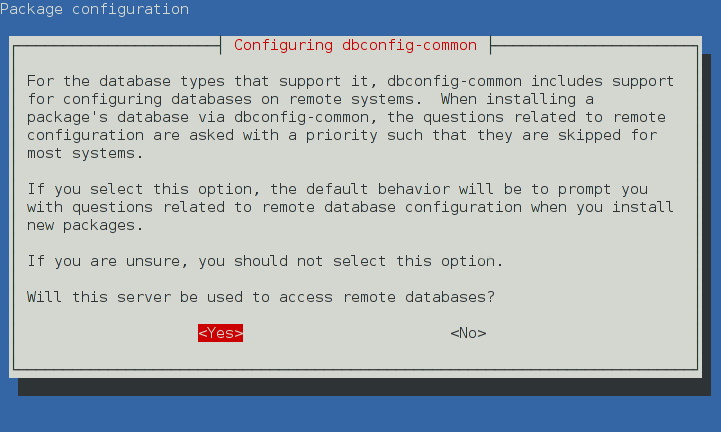
Unlike other debconf prompts, you cannot pre-seed the responses for the
dbconfig-common prompts by using debconf-set-selections. Instead,
you must create a file in /etc/dbconfig-common. For example, you
might create a keystone configuration file for dbconfig-common that is
located in /etc/dbconfig-common/keystone.conf, as follows:
dbc_install='true'
dbc_upgrade='true'
dbc_remove=''
dbc_dbtype='mysql'
dbc_dbuser='keystone'
dbc_dbpass='PASSWORD'
dbc_dbserver=''
dbc_dbport=''
dbc_dbname='keystonedb'
dbc_dbadmin='root'
dbc_basepath=''
dbc_ssl=''
dbc_authmethod_admin=''
dbc_authmethod_user=''
After you create this file, run this command:
# apt-get install keystone
The Identity service is installed with MySQL as the database back end,
keystonedb as database name, and the localhost socket file. The
corresponding DSN (Database Source Name) will then be:
[database]
connection = mysql+pymysql://keystone:PASSWORD@localhost/keystonedb
The dbconfig-common package will configure MySQL for these access
rights, and create the database for you. Since OpenStack 2014.1.1, all
OpenStack packages in Debian are performing the following MySQL query
after database creation (if you decide to use MySQL as a back-end):
ALTER DATABASE keystone CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci
So, if using Debian, you wont need to care about database creation, access rights and character sets. All that is handled for you by the packages.
As an example, here are screenshots from the cinder-common package:
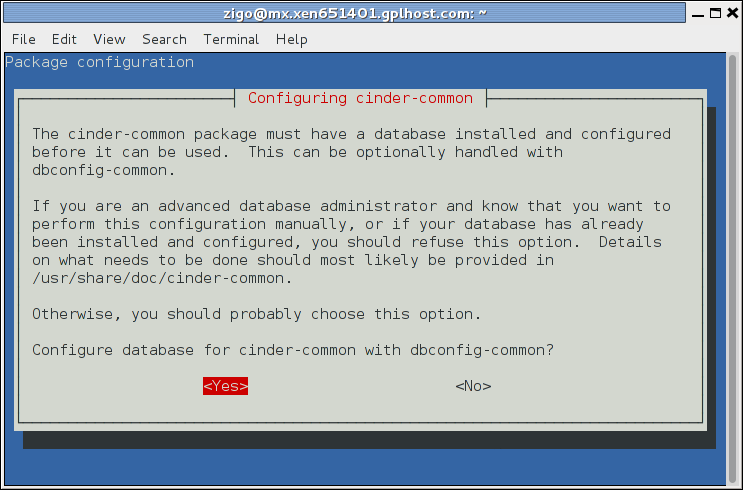
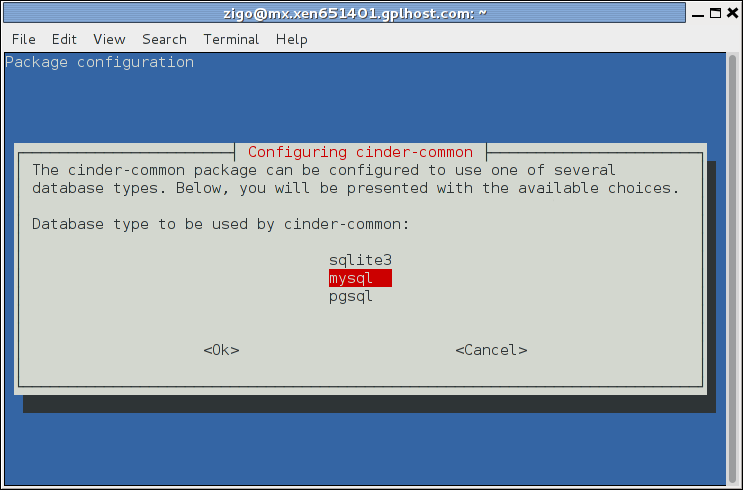

By default in Debian, you can access the MySQL server from either
localhost through the socket file or 127.0.0.1. To access it over the
network, you must edit the /etc/mysql/my.cnf file, and the
mysql.user table. To do so, Debian provides a helper script in the
openstack-deploy package. To use it, install the package:
# apt-get install openstack-deploy
and run the helper script:
# /usr/share/openstack-deploy/mysql-remote-root
Alternatively, if you do not want to install this package, run this script to enable remote root access:
#!/bin/sh
set -e
SQL="mysql --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf -Dmysql -e"
ROOT_PASS=`${SQL} "SELECT Password FROM user WHERE User='root' LIMIT 1;" \
| tail -n 1`
${SQL} "REPLACE INTO user SET host='%', user='root',\
password='${ROOT_PASS}', Select_priv='Y', Insert_priv='Y',\
Update_priv='Y', Delete_priv='Y', Create_priv='Y', Drop_priv='Y',\
Reload_priv='Y', Shutdown_priv='Y', Process_priv='Y', File_priv='Y',\
Grant_priv='Y', References_priv='Y', Index_priv='Y', Alter_priv='Y',\
Super_priv='Y', Show_db_priv='Y', Create_tmp_table_priv='Y',\
Lock_tables_priv='Y', Execute_priv='Y', Repl_slave_priv='Y',\
Repl_client_priv='Y', Create_view_priv='Y', Show_view_priv='Y',\
Create_routine_priv='Y', Alter_routine_priv='Y', Create_user_priv='Y',\
Event_priv='Y', Trigger_priv='Y' "
${SQL} "FLUSH PRIVILEGES"
sed -i 's|^bind-address[ \t]*=.*|bind-address = 0.0.0.0|' /etc/mysql/my.cnf
/etc/init.d/mysql restart
You must enable remote access before you install OpenStack services on multiple nodes.

Except where otherwise noted, this document is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. See all OpenStack Legal Documents.