[ English | русский | Indonesia ]
Metal networking¶
OpenStack-Ansible supports deploying OpenStack and related services on “metal” as well as inside LXC containers. Python virtual environments (venvs) provide OpenStack service and Python library segregation, while other services such as Galera and RabbitMQ are co-located on the host. All services in this deployment model share the same IP address.
This appendix describes how the interfaces are connected and how traffic flows.
For more information about how the OpenStack Networking service (Neutron) uses the interfaces for instance traffic, please see the OpenStack Networking Guide.
For details on the configuration of networking for your environment, please have a look at openstack_user_config settings reference.
Physical host interfaces¶
In a typical production environment, physical network interfaces are combined in bonded pairs for better redundancy and throughput. Avoid using two ports on the same multiport network card for the same bonded interface, because a network card failure affects both of the physical network interfaces used by the bond. Multiple bonded interfaces (ie. bond0, bond1) can be used to segregate traffic, if desired. Single (bonded) interfaces are also a supported configuration, but will require the use of VLAN subinterfaces.
Linux Bridges/Switches¶
The combination of containers and flexible deployment options requires implementation of advanced Linux networking features, such as bridges, switches, and namespaces.
Bridges provide layer 2 connectivity (similar to switches) among physical, logical, and virtual network interfaces within a host. After a bridge/switch is created, the network interfaces are virtually plugged in to it.
OpenStack-Ansible uses Linux bridges for control plane connections to LXC containers, and can use Linux bridges or Open vSwitch-based bridges for data plane connections that connect virtual machine instances to the physical network infrastructure.
Network namespaces provide logically separate layer 3 environments (similar to VRFs) within a host. Namespaces use virtual interfaces to connect with other namespaces, including the host namespace. These interfaces, often called
vethpairs, are virtually plugged in between namespaces similar to patch cables connecting physical devices such as switches and routers.
Network diagrams¶
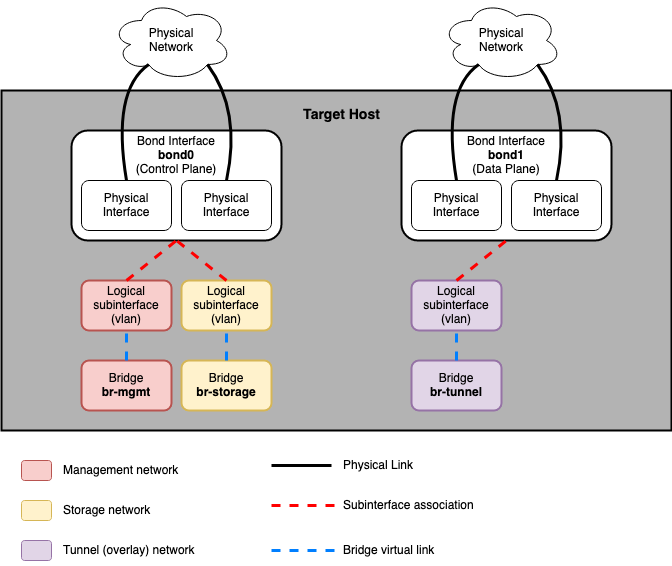
Hosts with services running on metal¶
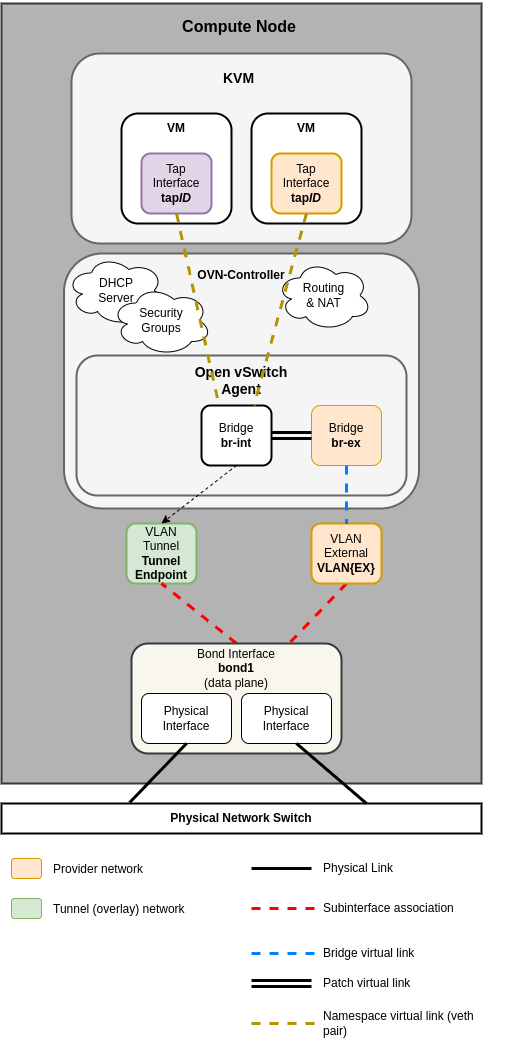
The following diagram shows how all of the interfaces and bridges interconnect to provide network connectivity to the OpenStack deployment:
Neutron traffic¶
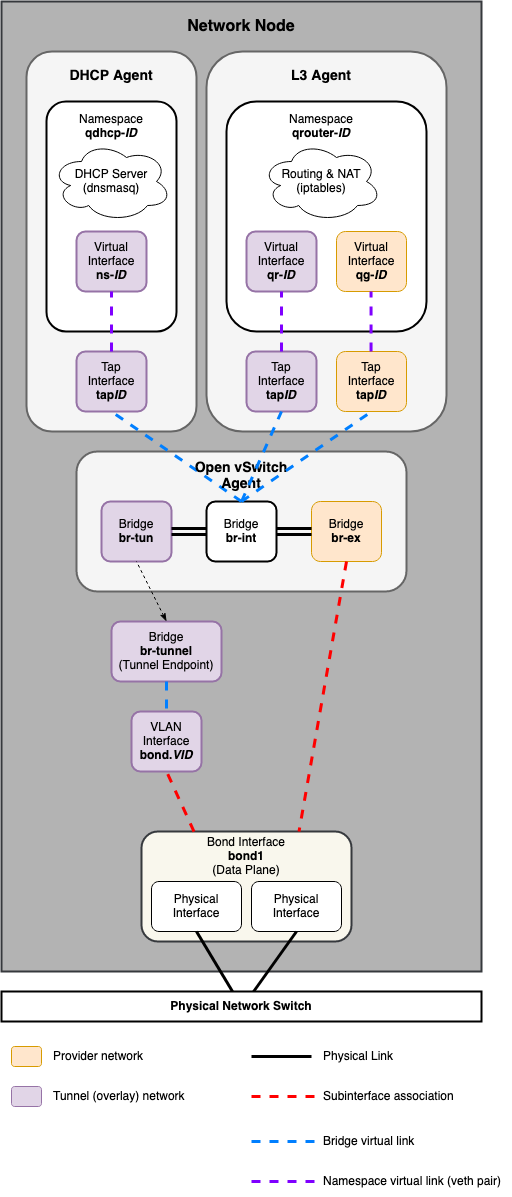
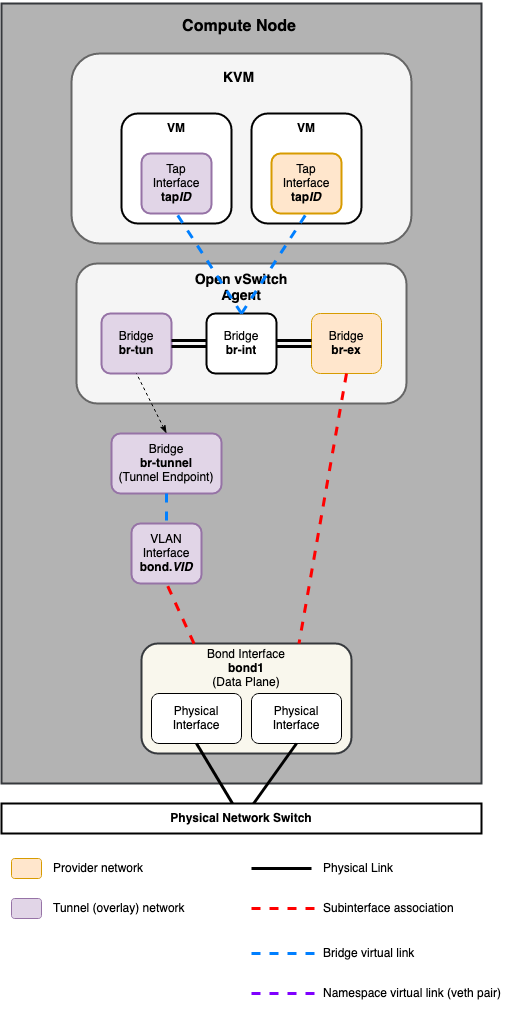
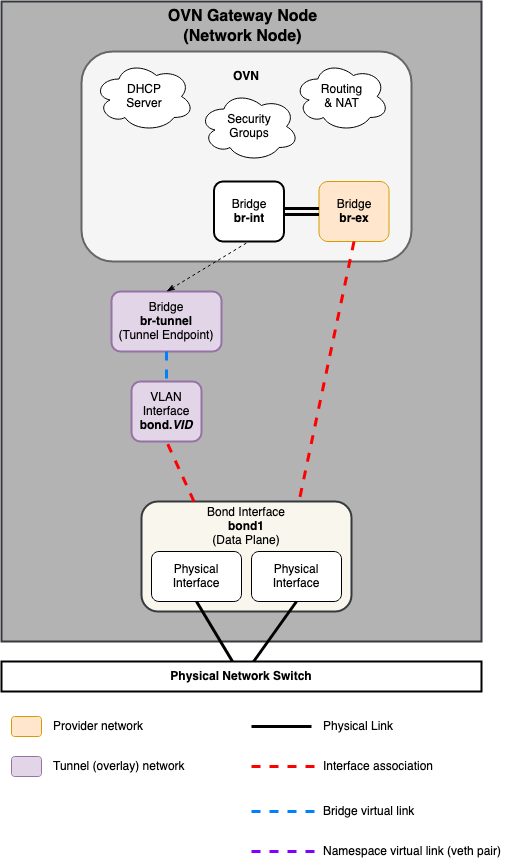
Common reference drivers, including ML2/OVS, and ML2/OVN, and their respective agents, are responsible for managing the virtual networking infrastructure on each node. OpenStack-Ansible refers to Neutron traffic as “data plane” traffic, and can consist of flat, VLAN, or overlay technologies such as VXLAN and Geneve.
Neutron agents can be deployed across a variety of hosts, but are typically limited to dedicated network hosts or infrastructure hosts (controller nodes). Neutron agents are deployed “on metal” and not within an LXC container. Neutron typically requires the operator to define “provider bridge mappings”, which map a provider network name to a physical interface. These provider bridge mappings provide flexibility and abstract physical interface names when creating provider networks.
Open vSwitch/OVN Example:
bridge_mappings = physnet1:br-ex
OpenStack-Ansible provides two overrides when defining provider networks that can be used for creating the mappings and in some cases, connecting the physical interfaces to provider bridges:
host_bind_overridenetwork_interface
The host_bind_override key is used to replace an LXC-related interface
name with a physical interface name when a component is deployed on bare metal hosts.
It will be used to populate network_mappings for Neutron.
The network_interface override is used for Open vSwitch and OVN-based deployments,
and requires a physical interface name which will be connected to the provider bridge
(ie. br-ex) for flat and vlan-based provider and project network traffic.
The following diagrams reflect the differences in the virtual network layout for supported network architectures.
Open vSwitch (OVS)¶
Networking Node¶
Compute Node¶
Open Virtual Network (OVN)¶
Note
The ML2/OVN mechanism driver is deployed by default as of the Zed release of OpenStack-Ansible.
Networking Node¶
Compute Node¶