6.7. Fuel Containerized Control Plane performance report¶
- Abstract
This document includes Fuel CCP control plane performance test results for various environments (from 50 to 350 nodes). All tests have been performed regarding Fuel Containerized Control Plane performance testing
6.7.1. Environment description¶
For Kubernetes pre-deployment Kargo tool was used. More information about fuel-ccp and how it can be installed can be found in official documentation.
6.7.1.1. Hardware configuration of each server¶
All servers have 3 types of configuration describing in table below
server |
vendor,model |
Dell PowerEdge R630 |
CPU |
vendor,model |
Intel,E5-2680 v3 |
processor_count |
2 |
|
core_count |
12 |
|
frequency_MHz |
2500 |
|
RAM |
vendor,model |
Samsung, M393A2G40DB0-CPB |
amount_MB |
262144 |
|
NETWORK |
interface_name s |
eno1, eno2 |
vendor,model |
Intel,X710 Dual Port |
|
bandwidth |
10G |
|
interface_names |
enp3s0f0, enp3s0f1 |
|
vendor,model |
Intel,X710 Dual Port |
|
bandwidth |
10G |
|
STORAGE |
dev_name |
/dev/sda |
vendor,model |
raid1 - Dell, PERC H730P Mini
2 disks Intel S3610
|
|
SSD/HDD |
SSD |
|
size |
3,6TB |
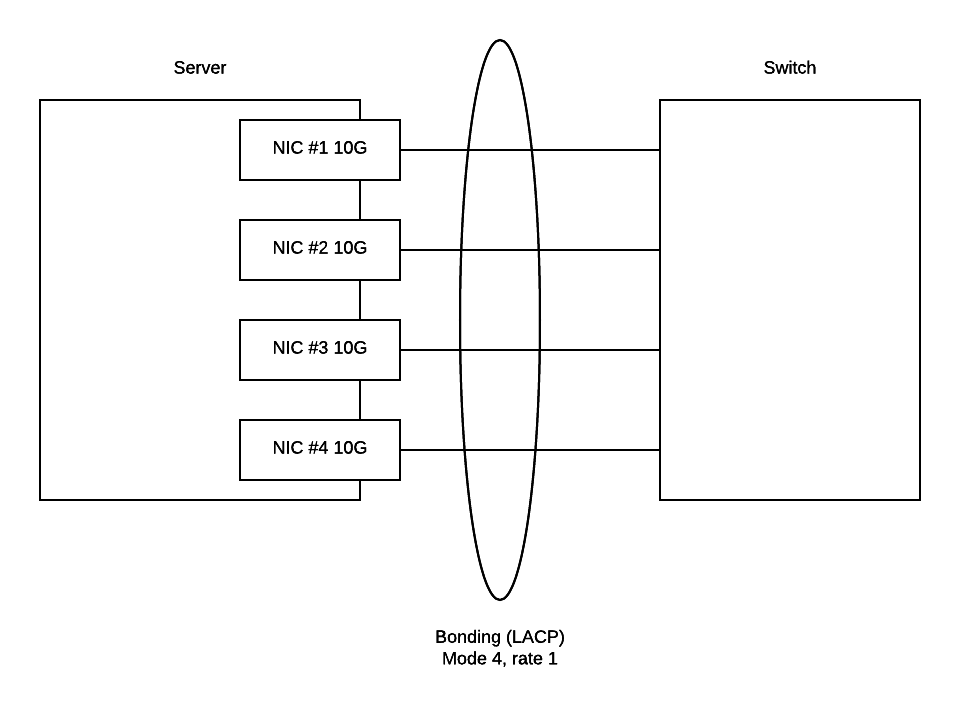
6.7.1.2. Network configuration of each server¶
All servers have same network configuration:
6.7.2. Test results¶
6.7.2.1. Test Case 1: Boot and delete server¶
The following set of results is dedicated to investigate how Nova installed against Kubernetes cluster via fuel-ccp tool is behaving on various scale.
6.7.2.1.1. 200 nodes OpenStack cluster, concurrency 5, 910 iterations¶
NovaServers.boot_and_delete_server scenario in
nova_200_nodes.html
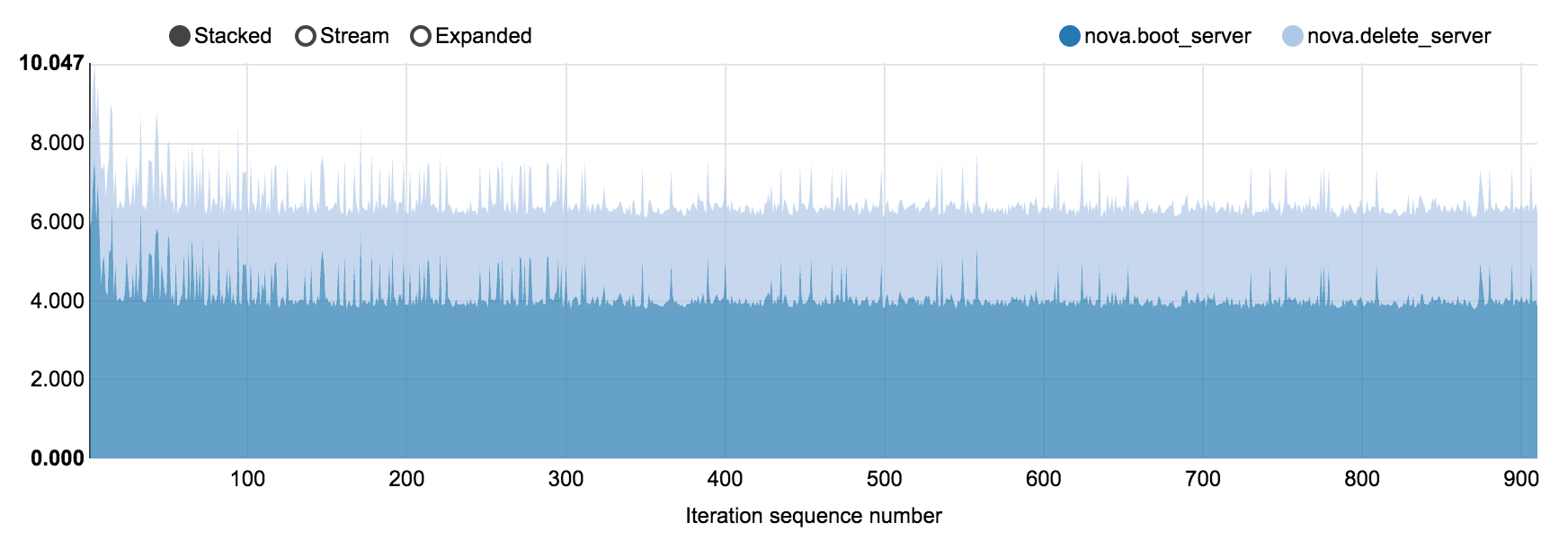
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
boot_server |
4.001 |
5.001 |
5.135 |
7.686 |
3.785 |
delete_server |
2.346 |
2.487 |
2.517 |
3.769 |
2.297 |
6.7.2.1.2. 350 nodes OpenStack cluster, concurrency 5, 1750 iterations¶
NovaServers.boot_and_delete_server scenario in
nova_350_nodes.html
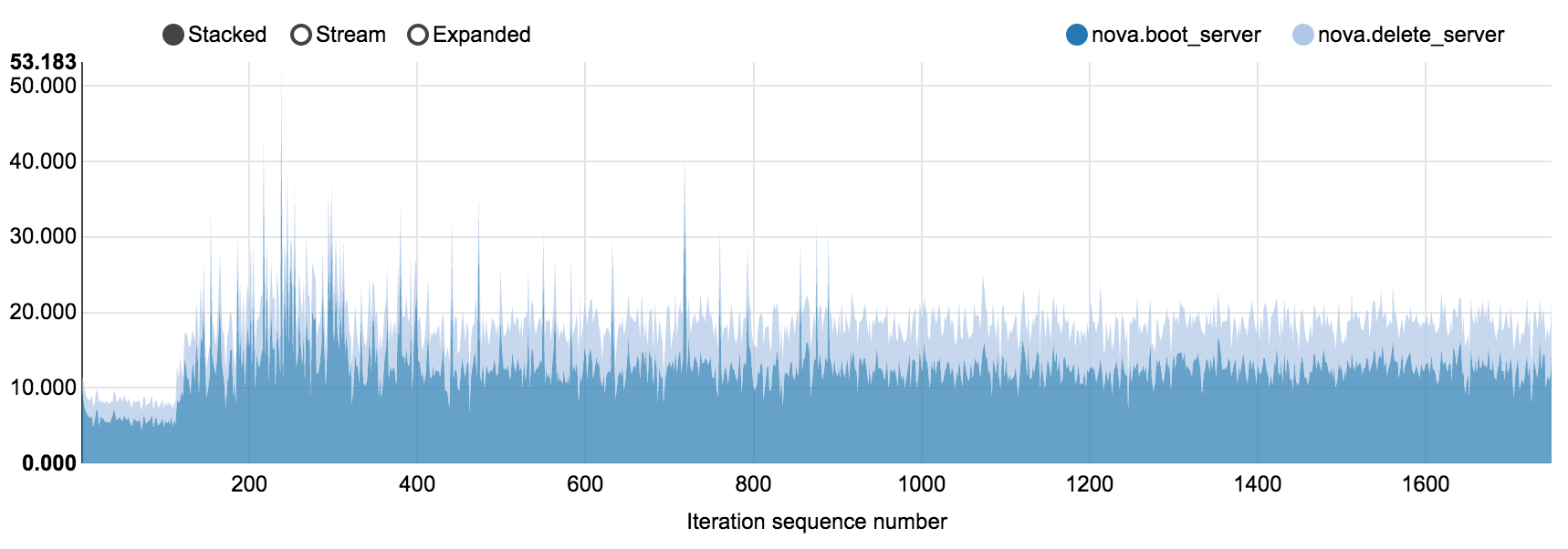
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
boot_server |
12.679 |
16.853 |
18.539 |
71.071 |
3.899 |
delete_server |
6.261 |
8.365 |
8.613 |
14.747 |
0.842 |
6.7.2.2. Test Case 2: Boot and list servers¶
The following set of results is dedicated to investigate how Nova installed against Kubernetes cluster via fuel-ccp tool is behaving on various scale.
6.7.2.2.1. 150 nodes OpenStack cluster, concurrency 20, 5520 iterations¶
Tested density: 40 VMs per compute node
NovaServers.boot_and_list_server scenario in
nova_150_nodes_20.html
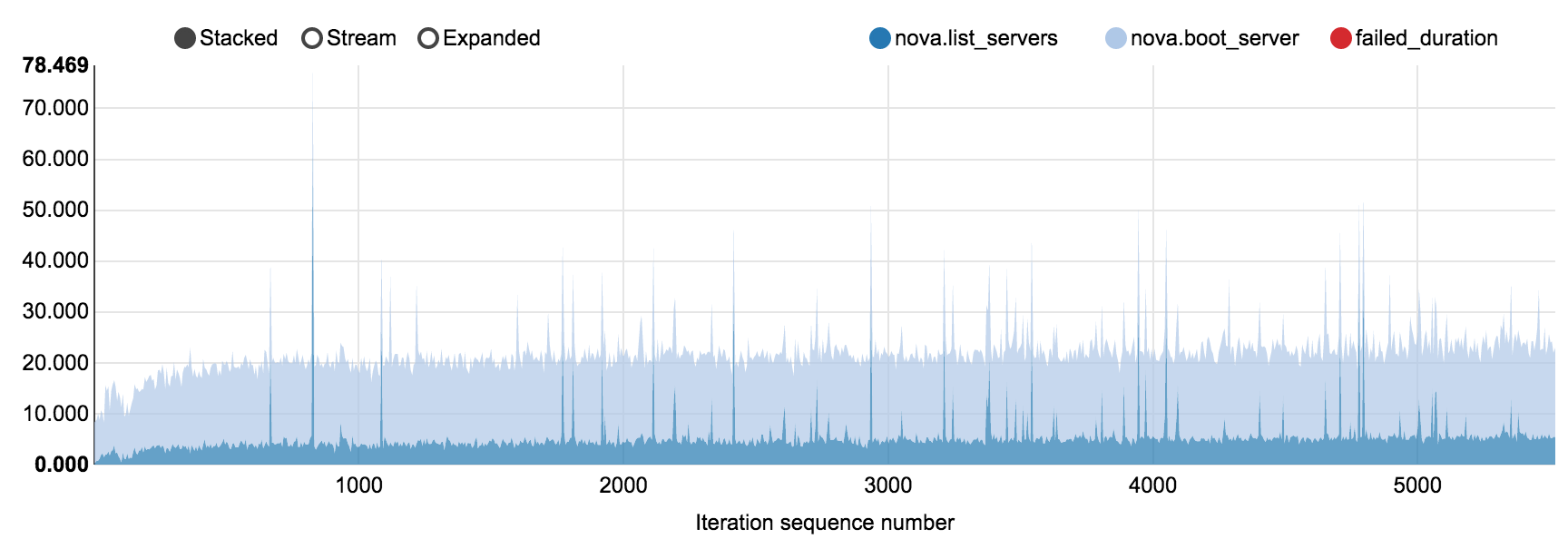
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
list_servers |
4.381 |
7.135 |
7.69 |
172.788 |
0.105 |
boot_server |
16.931 |
21.05 |
22.203 |
102.507 |
4.717 |
6.7.2.2.2. 150 nodes OpenStack cluster, concurrency 40, 5520 iterations¶
Tested density: 40 VMs per compute node
NovaServers.boot_and_list_server scenario in
nova_150_nodes_40.html
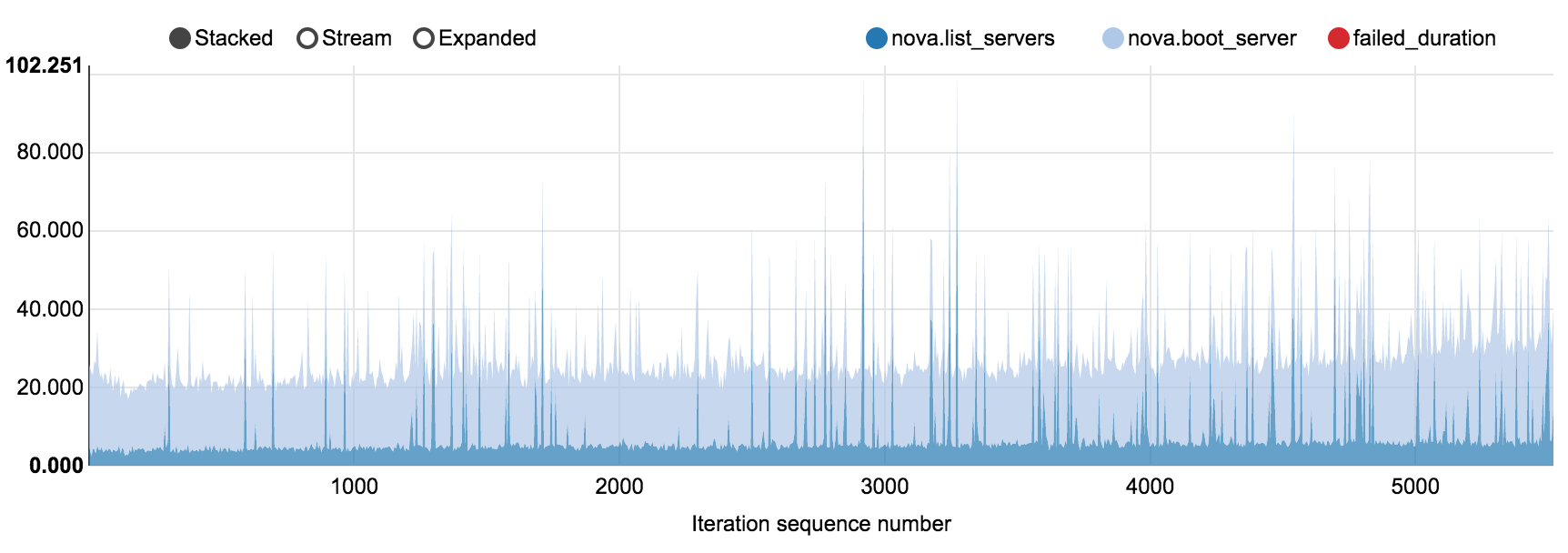
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
list_servers |
4.656 |
7.607 |
7.963 |
166.783 |
0.188 |
boot_server |
19.773 |
25.958 |
29.396 |
197.92 |
9.574 |
6.7.2.2.3. 200 nodes OpenStack cluster, concurrency 5, 910 iterations¶
Tested density: 5 VMs per compute node
NovaServers.boot_and_list_server scenario in
nova_200_nodes.html
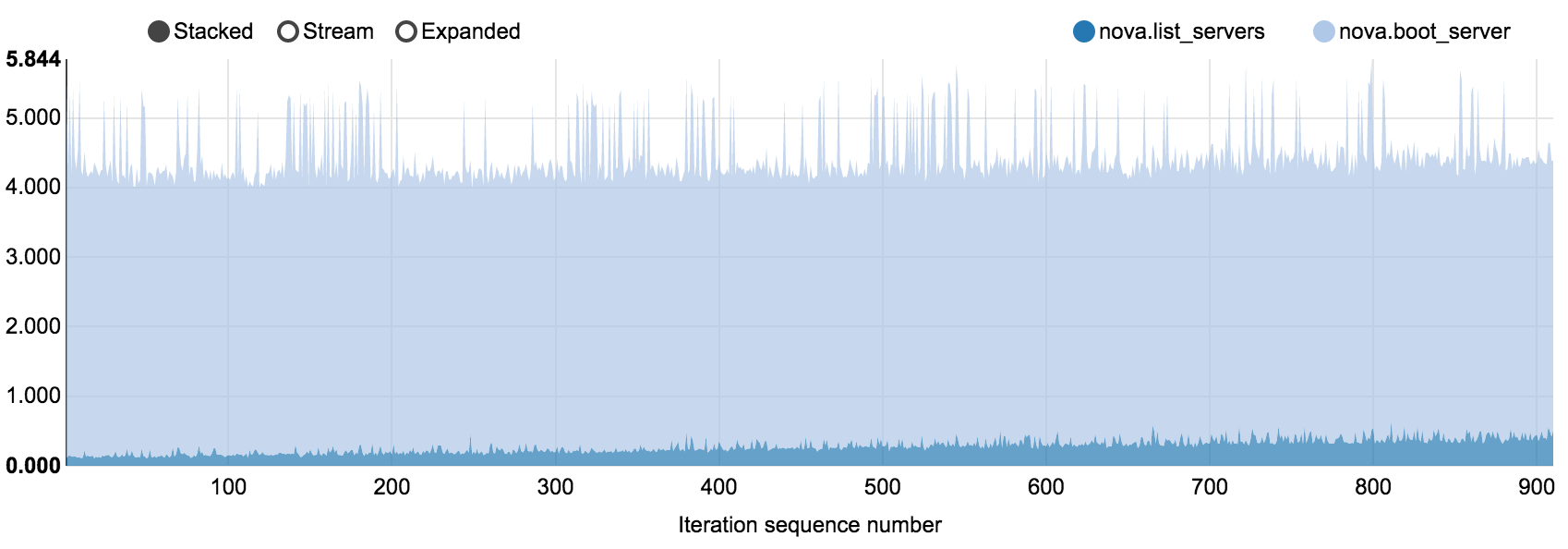
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
list_servers |
0.272 |
0.424 |
0.476 |
0.644 |
0.106 |
boot_server |
4.017 |
5.037 |
5.13 |
5.437 |
3.794 |
6.7.2.2.4. 200 nodes OpenStack cluster, concurrency 40, 7280 iterations¶
Tested density: 40 VMs per compute node
NovaServers.boot_and_list_server [2] scenario in
nova_200_nodes.html
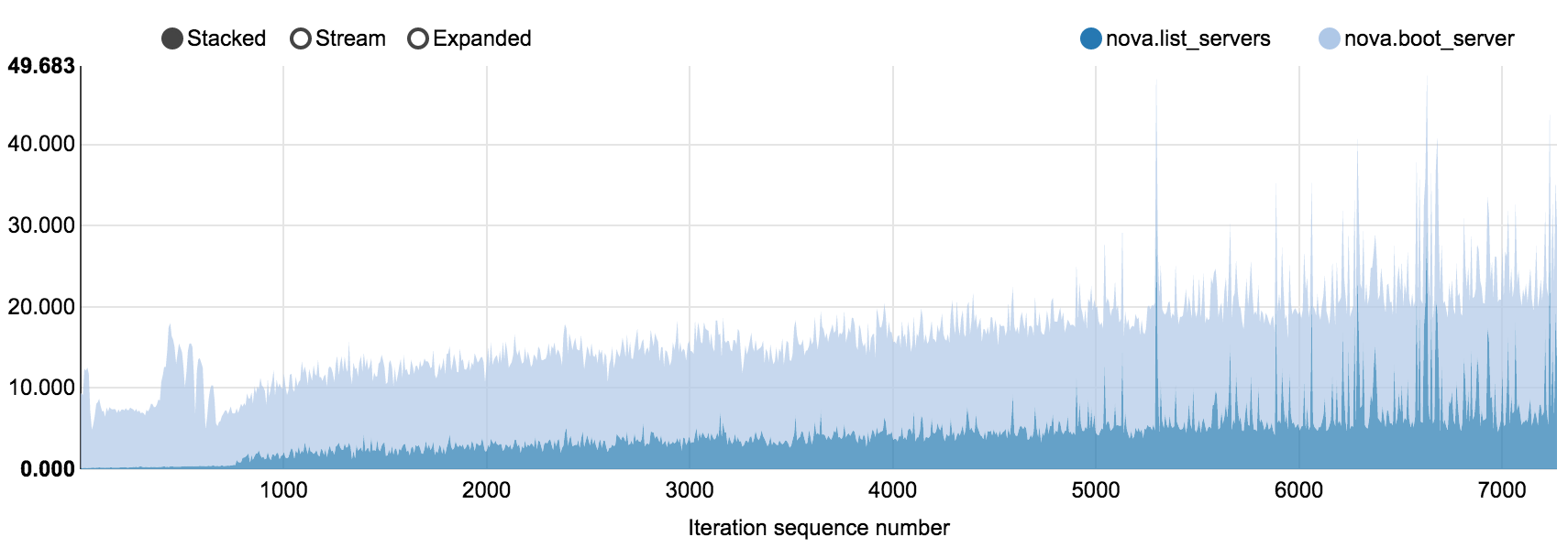
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
list_servers |
4.237 |
5.944 |
7.994 |
130.39 |
0.111 |
boot_server |
11.978 |
15.767 |
17.764 |
55.431 |
3.911 |
6.7.2.3. Test case 3: Keystone authentication¶
The following set of results is dedicated to investigate how Keystone installed
against Kubernetes cluster via fuel-ccp tool is behaving under various requests
per second load. For more information the full Rally report can be used:
keystone.html. Failed scenarios are
related either to the Keystone configuration tuning under Containerized Control
Plane repository or to the huge enough RPS being set for all in one Keystone.
6.7.2.3.1. 50 nodes OpenStack cluster, 30 RPS, 12000 iterations¶
Authenticate.keystone [4] scenario in
keystone.html
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
authenticate |
0.08 |
0.102 |
0.113 |
1.015 |
0.06 |
6.7.2.3.2. 50 nodes OpenStack cluster, 60 RPS, 12000 iterations¶
Authenticate.keystone [6] scenario in
keystone.html
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
authenticate |
0.097 |
0.132 |
0.147 |
1.113 |
0.073 |
6.7.2.3.3. 50 nodes OpenStack cluster, 90 RPS, 12000 iterations¶
Authenticate.keystone [5] scenario in
keystone.html
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
authenticate |
0.128 |
0.179 |
0.199 |
1.111 |
0.082 |
6.7.2.3.4. 50 nodes OpenStack cluster, 120 RPS, 12000 iterations¶
Authenticate.keystone [7] scenario in
keystone.html
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
authenticate |
0.195 |
0.269 |
0.298 |
1.455 |
0.096 |
6.7.2.3.5. 50 nodes OpenStack cluster, 150 RPS, 12000 iterations¶
Authenticate.keystone scenario in
keystone.html
Operation |
Median (sec) |
90%ile (sec) |
95%ile (sec) |
Max (sec) |
Min (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
authenticate |
0.478 |
0.738 |
0.817 |
2.024 |
0.109 |
